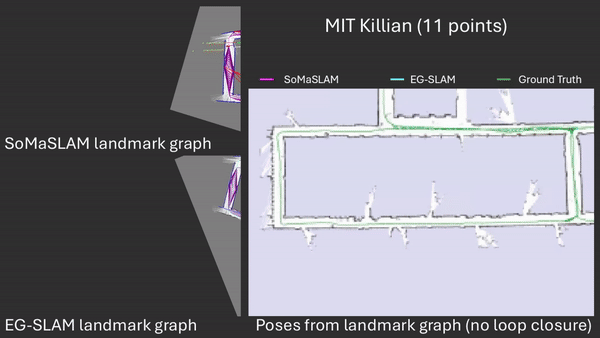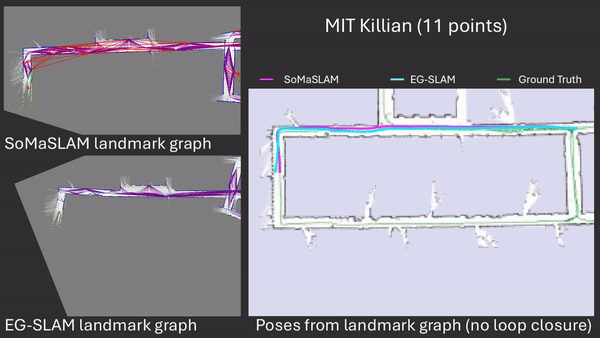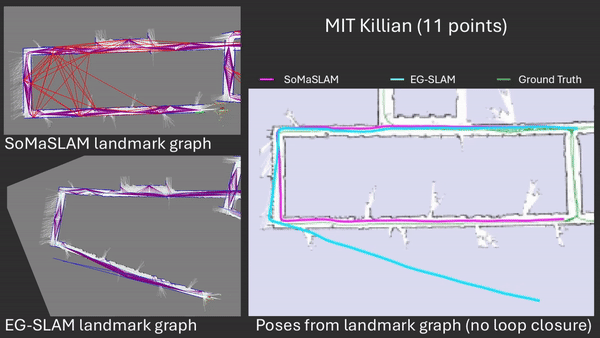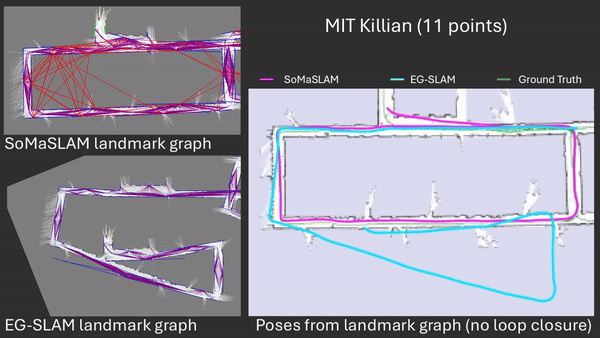
SoMaSLAM decreases pose error accumulation by using its unique constraints, sometimes achieving pose results close to the ground truth without loop closures.
We propose a graph SLAM algorithm for sparse range sensing that incorporates a soft Manhattan world utilizing landmark-landmark constraints. Sparse range sensing is necessary for tiny robots that do not have the luxury of using heavy and expensive sensors. Existing SLAM methods dealing with sparse range sensing lack accuracy and accumulate drift error over time due to limited access to data points. Algorithms that cover this flaw using structural regularities, such as the Manhattan world (MW), have shortcomings when mapping real-world environments that do not coincide with the rules. We propose SoMaSLAM, a 2D graph SLAM designed for tiny robots with sparse range sensing. Our approach effectively maps sparse range data without enforcing strict structural regularities and maintains an adaptive graph. We implement the MW assumption as soft constraints, which we refer to as a soft Manhattan world. We propose novel soft landmark-landmark constraints to incorporate the soft MW into graph SLAM. Through extensive evaluation, we demonstrate that our proposed SoMaSLAM method improves localization accuracy on diverse datasets and is flexible enough to be used in the real world.
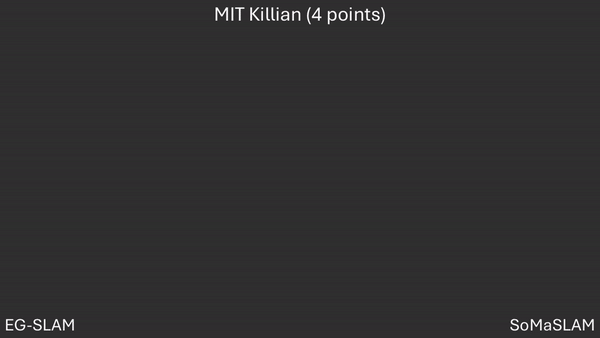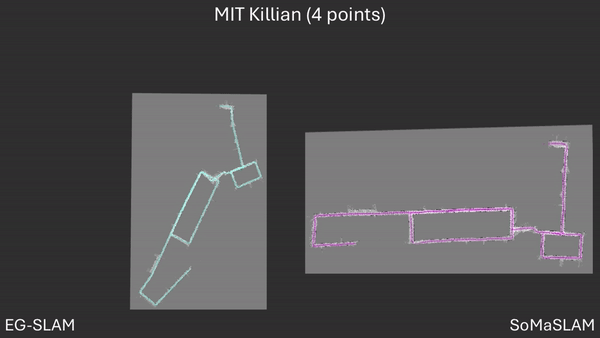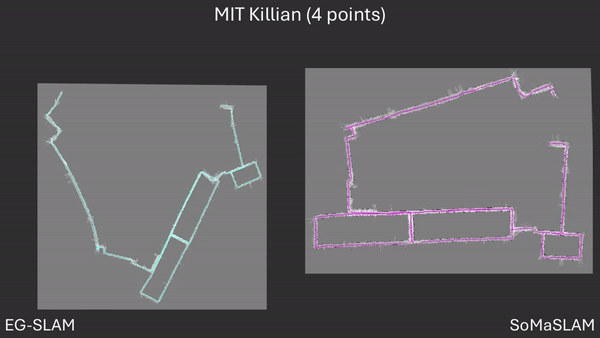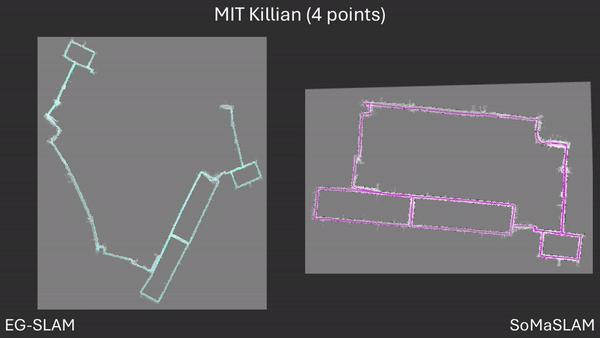
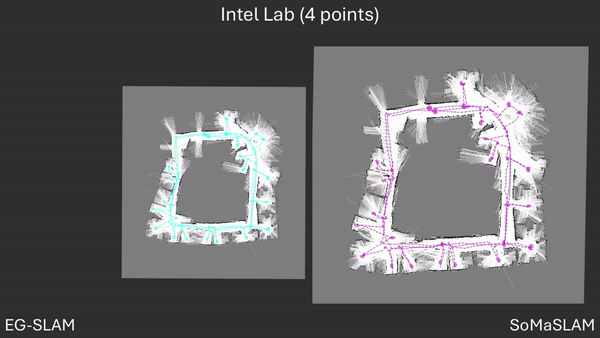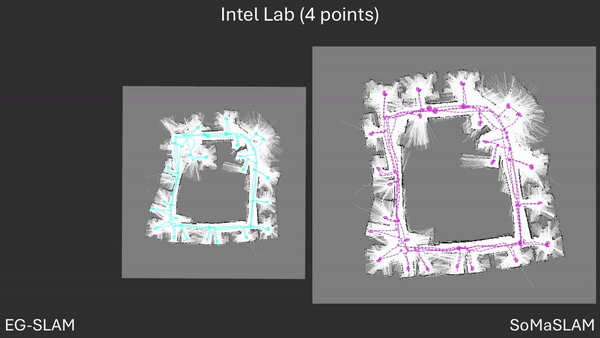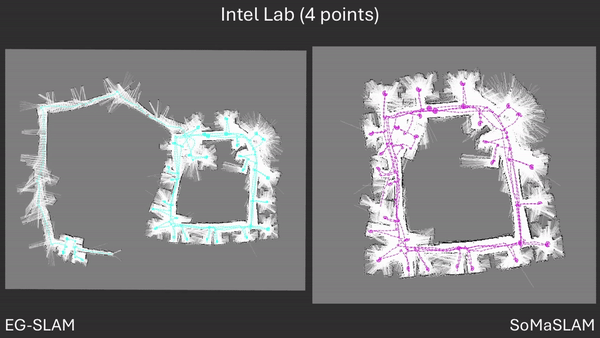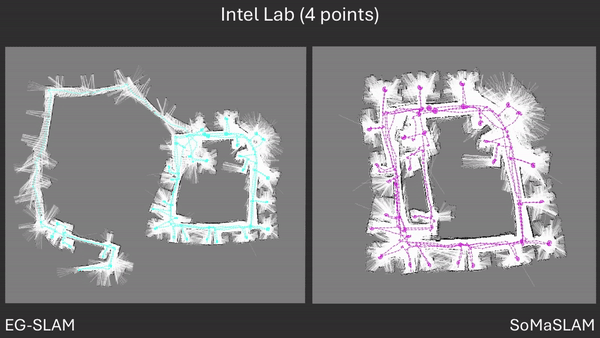
SoMaSLAM lessens error accumulation on the poses compared to EG-SLAM, achieving a more accurate graph.
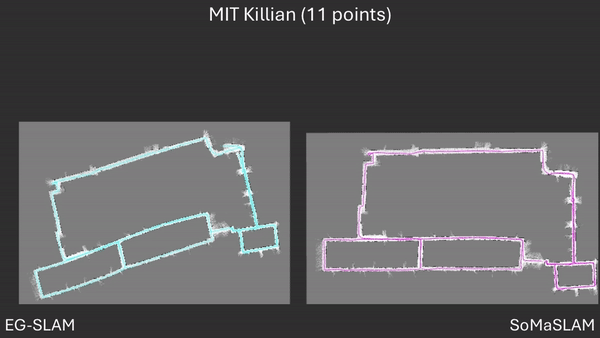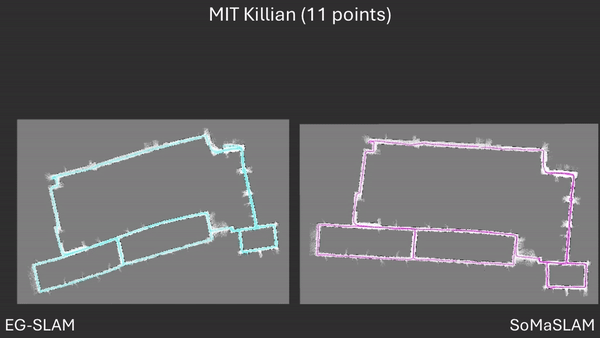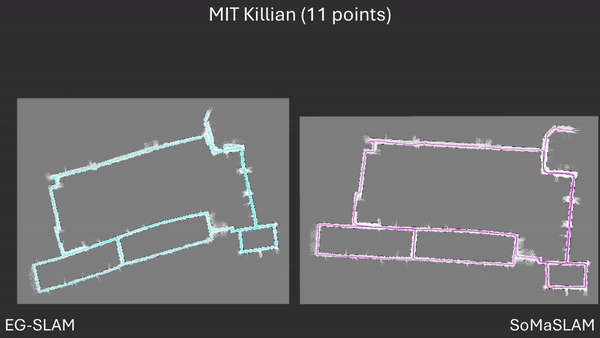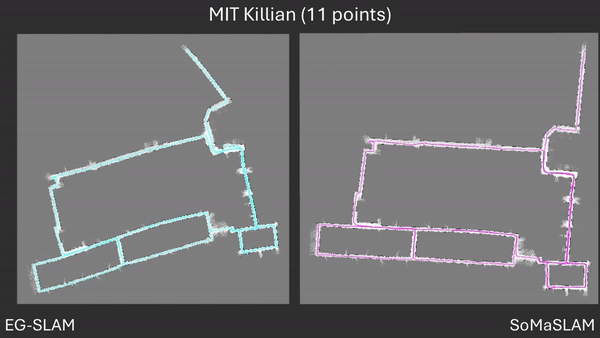
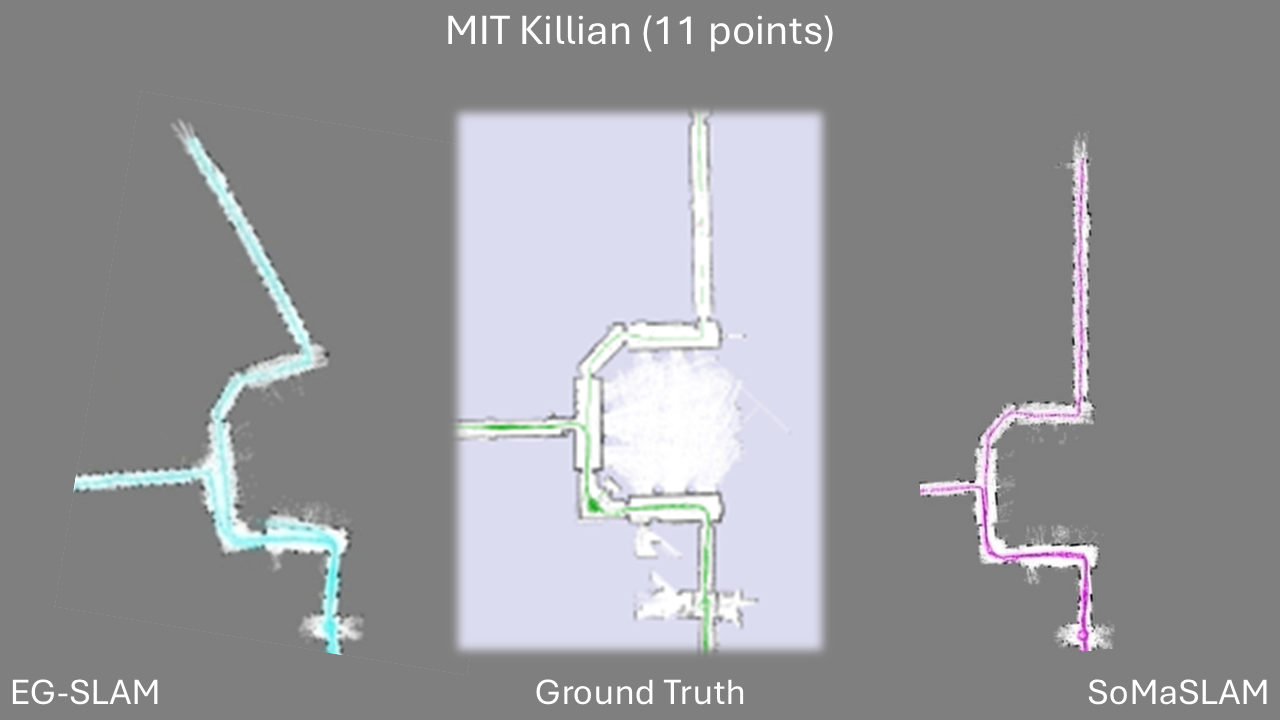
Comparison between EG-SLAM and SoMaSLAM regarding the C-shaped section.
Failing to complete a necessary loop closing is an extension of error accumulation. Too much accumulated error prevents necessary loop closing procedures from happening.
Our code and dataset will be released upon acceptance of our work.